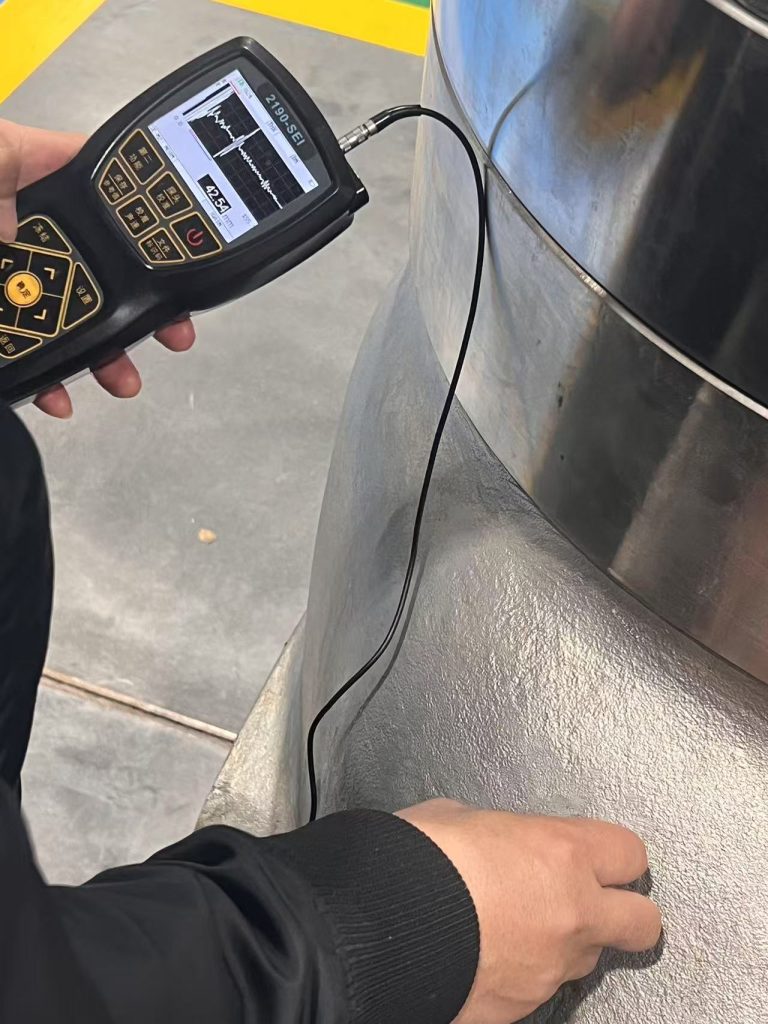
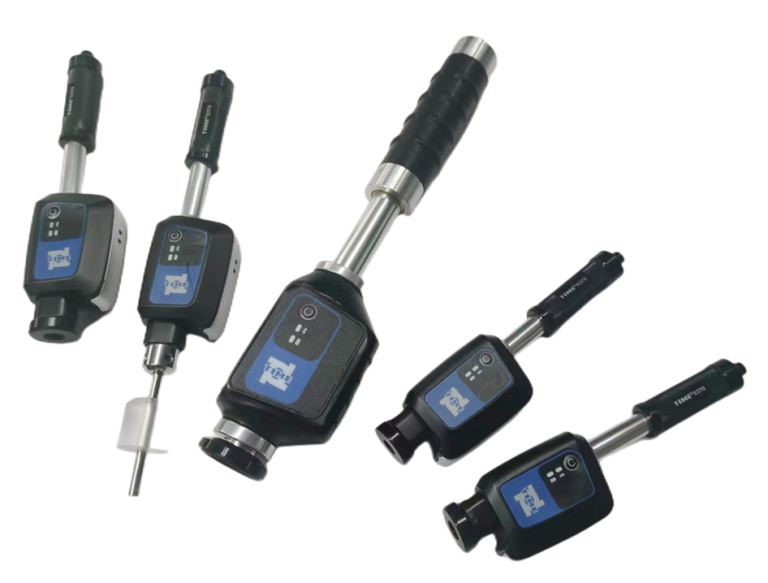
Calibrating a hardness tester is essential to ensure accurate and reliable measurements. Here are the steps to properly calibrate a hardness tester:
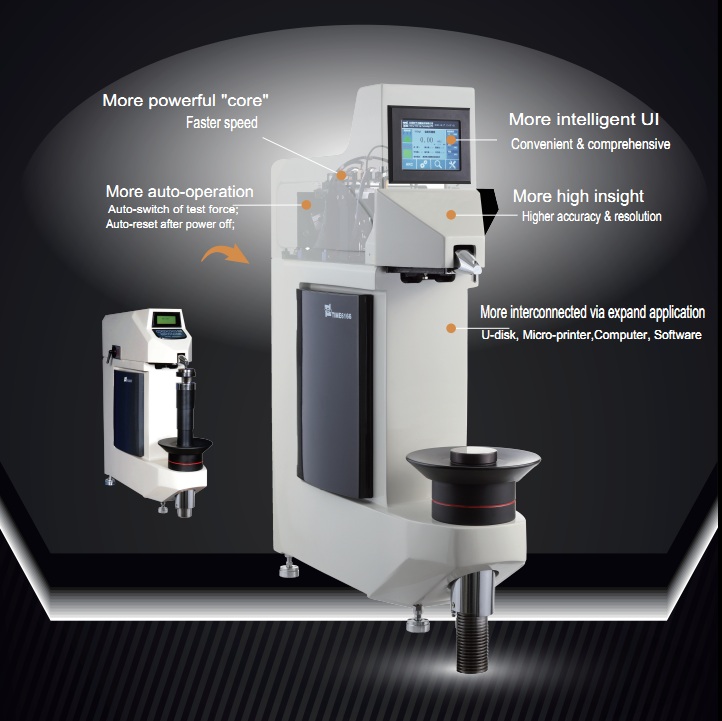

1. Check the manual: Before starting the calibration process, it is important to review the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific hardness tester model being used. The manual will provide guidance on the calibration procedure and any specific requirements.
2. Verify the reference standards: It is crucial to use certified reference standards that are traceable to a national or international standard. These standards should be in good condition and have a known hardness value.
3. Prepare the tester: Ensure that the hardness tester is clean and in good working condition before calibration. Check for any damage or wear on the testing head or indenters that could affect the accuracy of the measurements.
4. Perform zero calibration: Zero calibration is done to ensure that the tester is reading accurately at zero hardness. This step involves adjusting the tester to read zero when no force is applied to the indenter.
5. Perform calibration with reference standards: Using the reference standards, perform a series of hardness tests at different hardness values. Compare the readings from the tester to the known values of the reference standards. Adjust the tester as needed to ensure accurate readings.
6. Record the calibration results: Keep detailed records of the calibration process, including the reference standards used, the hardness values tested, and the readings from the hardness tester. This documentation is important for quality control and traceability.
7. Regularly check and recalibrate: It is important to regularly check the calibration of the hardness tester and recalibrate as needed. Factors such as wear and tear, environmental conditions, and usage can affect the accuracy of the tester over time.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your hardness tester is properly calibrated and providing accurate hardness measurements. Proper calibration is essential for maintaining the quality and reliability of hardness testing results.