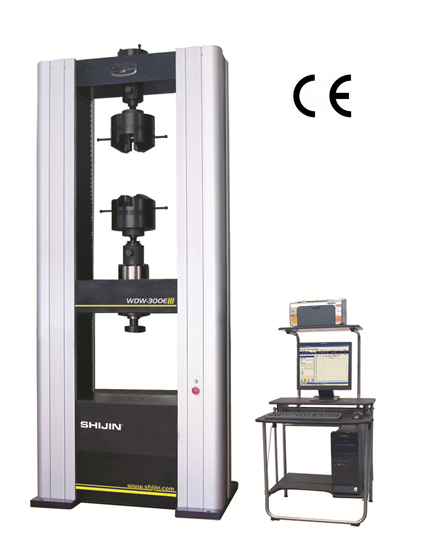
Hardness testing is a crucial step in determining the quality and durability of metal products. There are several methods that can be used to test the hardness of metals, each with its own advantages and limitations. In this article, we will explore the various hardness testing processes commonly used in the industry.
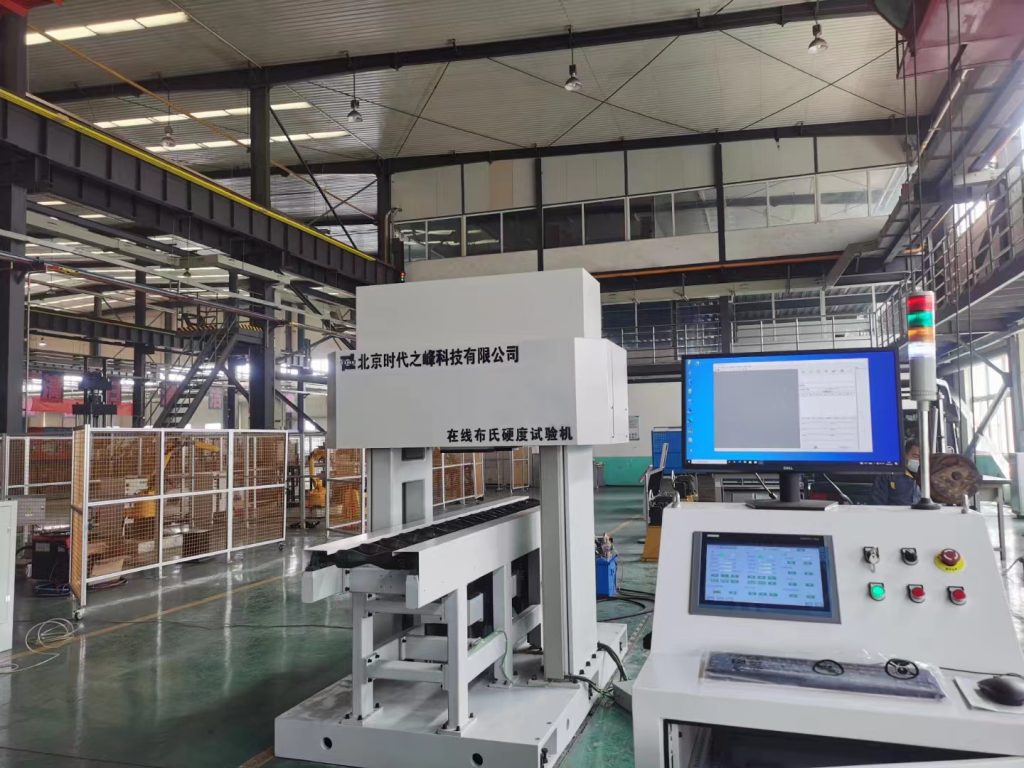

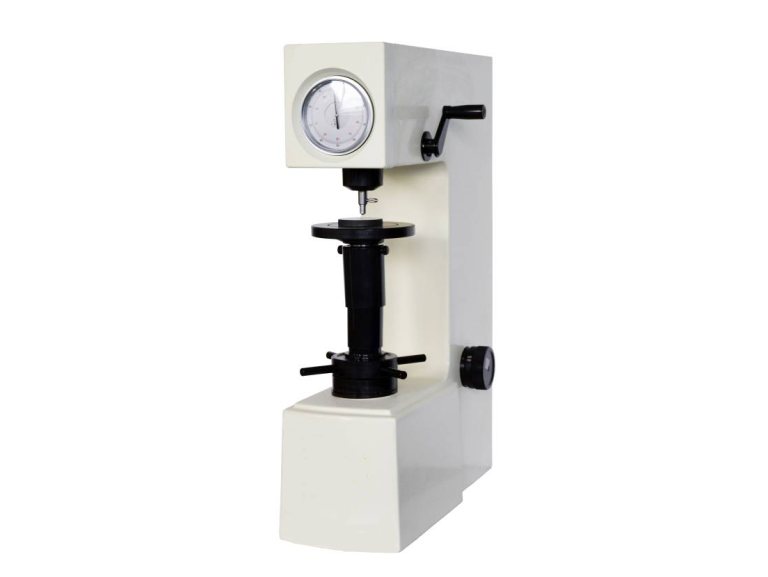
One of the most common methods of hardness testing is the Rockwell hardness test. This test involves applying a specific load to a metal surface using a hardened steel ball or a diamond cone. The depth of the indentation left on the metal surface is then measured to determine the hardness of the material. The Rockwell hardness test is widely used due to its simplicity and quick results.
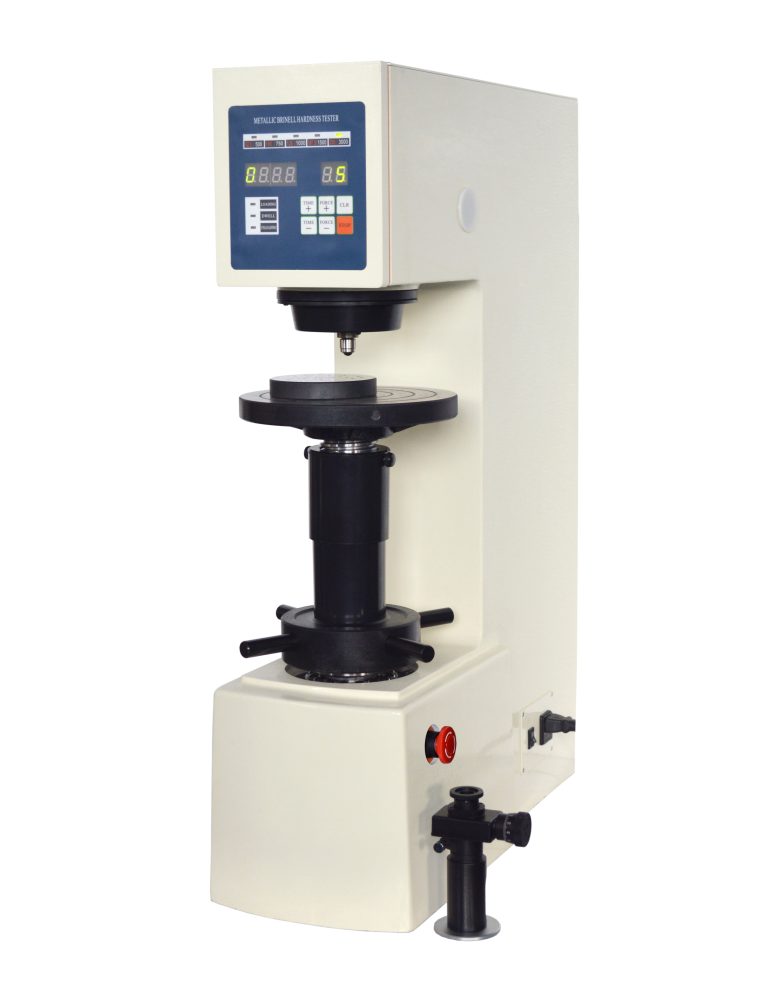
Another popular method of hardness testing is the Brinell hardness test. In this test, a hardened steel ball is pressed into the surface of the metal, and the diameter of the resulting indentation is measured. The Brinell hardness test is particularly useful for measuring the hardness of softer metals or materials with coarse grain structures.
Vickers hardness testing is another commonly used method that involves pressing a pyramid-shaped diamond into the surface of the metal. The size of the indentation left by the diamond is measured to determine the hardness of the material. Vickers hardness testing is often used for measuring the hardness of very hard materials or thin sections of metal.
In addition to these traditional hardness testing methods, there are also more advanced techniques such as microhardness testing and nanoindentation. Microhardness testing involves applying a very small load to the surface of the metal and measuring the resulting indentation size. This method is particularly useful for measuring the hardness of small or thin samples.
Nanoindentation is a cutting-edge technique that involves applying an extremely small load to the surface of the metal using a sharp diamond tip. The depth of the indentation is measured at the nanometer scale, allowing for precise measurements of hardness at the microstructural level. Nanoindentation is often used for research purposes or for measuring the hardness of very thin coatings.
Hardness testing is a critical process in the metal industry for ensuring the quality and reliability of metal products. By using a combination of traditional and advanced hardness testing methods, manufacturers can accurately measure the hardness of metals and make informed decisions about their properties and performance.