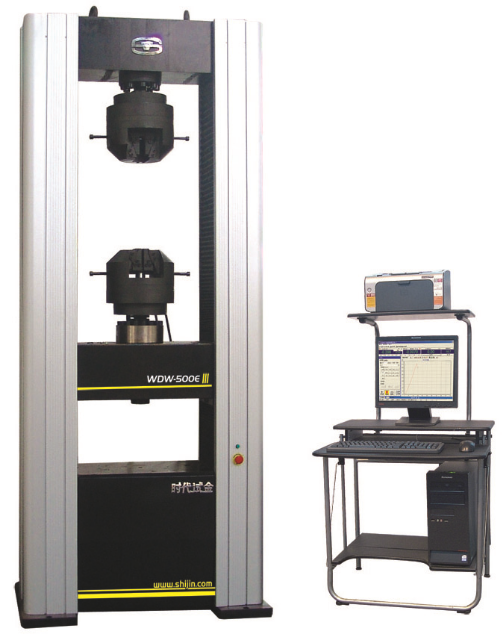
Hardness tests are generally divided into Brinell, Rockwell and Vickers. The Rockwell hardness tester has the characteristics of simple operation, accurate results, high work efficiency, and does not cause damage to the specimen. Therefore, it is widely used in laboratory and laboratory production processes.
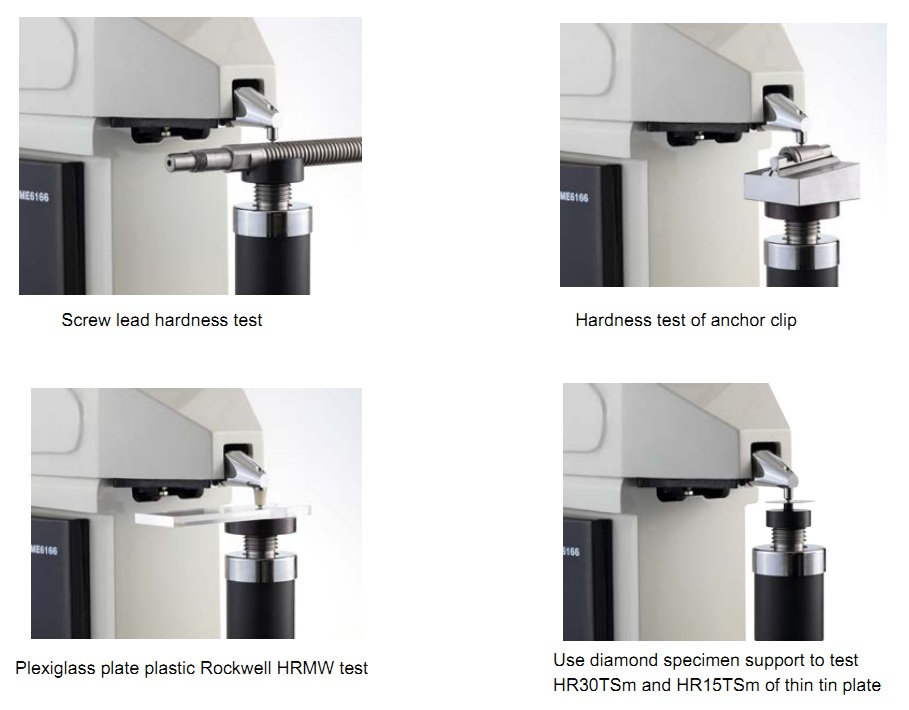

The correct use and precautions of Rockwell hardness tester are introduced below for reference.
- Rockwell hardness tester test principle
The Rockwell hardness test uses a special indenter (diamond indenter or steel ball indenter) to press into the surface of the metal being tested under the action of two loads (preload and total load). The total load P is the preload. The sum of corpse 0 (10kg) and main load P1 is P:P0+P1.
- Scope of use and labeling symbols
During the test, the pressure head and load values, marking symbols and effective measurement range can be selected according to the table. The most common combinations of pressure head and load applications:
1>A scale: The indenter is a conical diamond indenter with a vertex angle of 120°, and the total load is 60kg: used to measure metals with extremely high hardness exceeding HRC67 (such as tungsten carbide carbide, etc.), or the test piece is hard Thin plate materials and thin surface layers are not suitable for HRC applications.
2>B scale: steel ball indenter with a diameter of 1.588mm, a total load of 100kg. It is used to measure soft or medium hardness metals and unquenched steel products. The application range is HRB30~l00: when testing The hardness of the sample is lower than HRB30-100: When the hardness of the sample is lower than HRB30, creep phenomenon begins to occur in most cases, and the contact surface between the steel ball and the test piece is too large, and the measured results are inaccurate; when the hardness is higher than HRB100 ~~. The steel ball deforms greatly and the depth of pressing into the test piece is too shallow, and the measured results are inaccurate.
3>c scale: vertex angle is 120. Grid cone diamond indenter, total load is l50kg. Used to measure the hardness of steel products hardened by heat treatment. Application range HRC20-67. If the hardness of the sample is lower than HRC20, the indenter If the test piece is pressed very deeply, the error caused by the correct shape of the indenter will increase, so the measured results will be inaccurate; if the hardness of the sample is higher than HRC67, the indenter will be pressed very shallowly into the test piece, and the tip of the indenter will There is a lot of pressure on the calf, and the pressure head is easily damaged.
- Operation steps
(1) Prepare an operation; use a certified hardness tester; the thickness of the test piece is greater than 10 times the depth of the indentation; select a suitable workbench according to the shape of the test piece; select a suitable indenter and total load value.
(2) Place the specimen on the working table, rotate the handwheel to slowly raise the working table, and lift the pressure head 0.6mm. The small pointer on the indicator dial points at “3”, and the large pointer points at the marks C and Position B (if it’s a little bit off, you can turn the dial to align it);
(3) After the pointer position is aligned, the loading handle can be pulled forward. So that the main load is added to the pressure head;
(4) When the pointer stops rotating, the unloading handle can be pushed back to remove the main load;
(5) Read the corresponding value from the indicator – when using a diamond indenter, read according to the outer ring of the dial; when using a steel ball indenter, read according to the inner ring of the dial;
(6) Release the handwheel and lower the workbench, then move the specimen slightly and select a new position to continue the test. The distance between the centers of the two indentations should not be less than 3mm: for the same specimen, it is best to place them in different locations. Carry out no less than 3 tests to obtain reliable hardness values.