Ultrasonic flaw detection is a non-destructive testing (NDT) method widely used in various industries to identify internal and surface defects in materials. This technique employs high-frequency sound waves to penetrate the material being tested and detect any anomalies that may compromise its integrity. The application of ultrasonic flaw detectors is crucial in ensuring safety, reliability, and quality in manufacturing and maintenance processes.
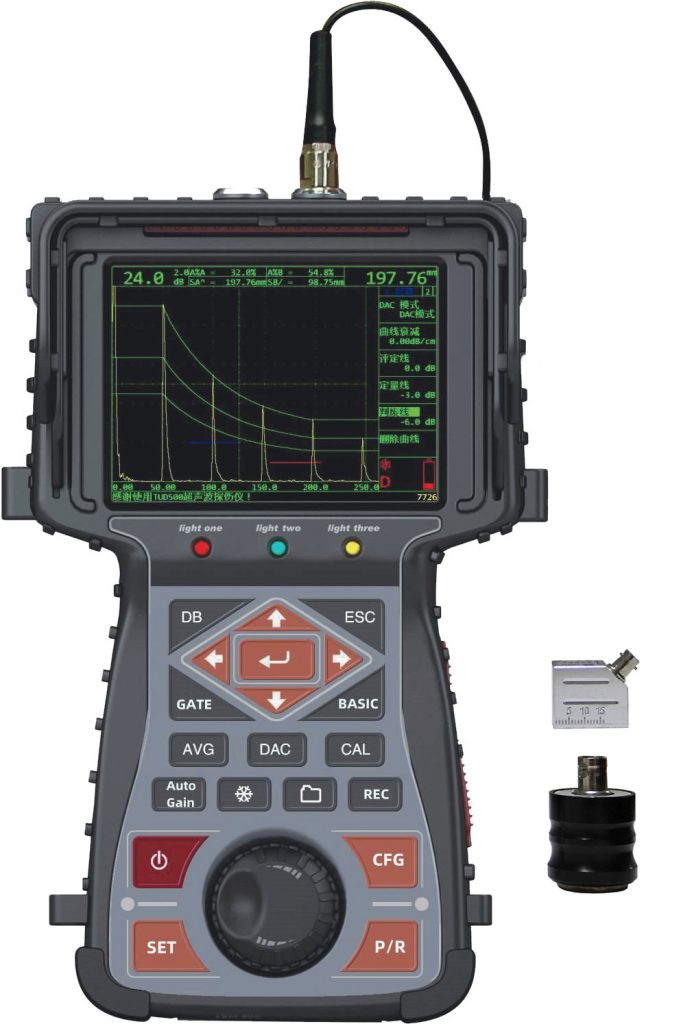

Principles of Ultrasonic Flaw Detection
Ultrasonic flaw detectors operate on the principle of sending ultrasonic waves into a material. When these waves encounter a boundary, such as a crack or void, they are reflected back to the sensor. The time taken for the echo to return is measured, allowing for the calculation of the distance to the defect. By analyzing the amplitude and shape of the reflected waves, operators can determine the size, shape, and type of flaw present.
Key Applications
1. Aerospace Industry: In the aerospace sector, the integrity of components is critical. Ultrasonic flaw detectors are used to inspect aircraft fuselages, wings, and engine components for cracks and other defects that could lead to catastrophic failures.
2. Oil and Gas: The oil and gas industry employs ultrasonic testing to assess the condition of pipelines, storage tanks, and pressure vessels. Regular inspections help prevent leaks and environmental disasters, ensuring the safety of operations.
3. Manufacturing: In manufacturing, ultrasonic flaw detectors are used to inspect welds, castings, and forgings. This application helps in maintaining quality control and ensuring that products meet industry standards.
4. Civil Engineering: Ultrasonic testing is applied to evaluate the integrity of concrete structures, such as bridges and dams. By detecting voids, delaminations, or cracks, engineers can assess the health of these structures and plan necessary repairs.
5. Railway Industry: Ultrasonic flaw detection is used to inspect railway tracks and components, ensuring safety in transportation. It helps identify internal flaws in rails and welds that could lead to derailments.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Flaw Detection
– Non-destructive: This method does not damage the material being tested, allowing for ongoing use after inspection.
– High sensitivity: Ultrasonic detectors can identify very small flaws that other NDT methods may miss.
– Depth penetration: Ultrasonic waves can penetrate thick materials, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
– Real-time results: The ability to provide immediate feedback makes it easier for operators to make quick decisions regarding maintenance and safety.
Challenges and Limitations
While ultrasonic flaw detection is a powerful tool, it does have limitations. The technique requires skilled operators who can interpret the results accurately. Additionally, certain materials, such as those with coarse grain structures, may pose challenges in detection. Surface conditions, such as roughness or coatings, can also affect the accuracy of the readings.
The application of ultrasonic flaw detectors is invaluable across various industries, enhancing safety and quality assurance processes. As technology advances, the capabilities of ultrasonic testing equipment continue to improve, leading to more reliable and accurate inspections. By integrating ultrasonic flaw detection into regular maintenance routines, industries can proactively address potential issues, ensuring the longevity and safety of their assets.